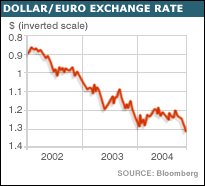
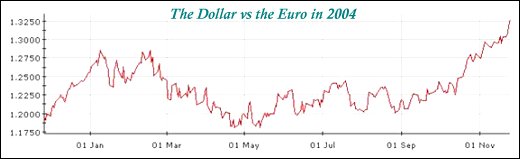
In international markets, all eyes are on the dollar, since uncertainty prevails about the depths to which it would decline. The currency, which appeared to have stabilised relative to the euro in early 2003, after declining from as far back as early 2002, has been sliding sharply since early September. The Financial Times reported on November 26 that the dollar had been through its seventh straight week of losses, falling to multi-year lows against the euro, yen and Swiss franc. Currently close to 1.3 euro and 102 yen to a dollar, the currency still seems heading downwards in the trading days to come.
| |
|
The principal factor being quoted to explain the weakness of the dollar
is the $570 billion annual current account deficit on the US balance of
payments. This makes the American appetite for international capital inflows
to finance its balance of payments insatiable. With the US fiscal deficit
running high and delivering output growth even if not jobs, there is no
corrective in sight for the current deficit which is seen as unsustainable.
The difficulty with this argument is that the deficit in the US balance
of payments is not new, nor is it a phenomenon specific to recent years
of rising fiscal deficits. Prior to that, consumer spending, fuelled by
debt, tax-cuts and the so-called "wealth effect" of a booming
stock market, triggered growth. This too was accompanied by rising trade
and current account deficits. Thus, the fundamental problem is that the
US economy is not competitive enough to prevent a substantial leakage
of domestic demand abroad and garner a significant share of world markets.
Growth is inevitably accompanied by external deficits, making the stimulus
required for any given level of domestic growth that much larger.
For long this was not seen as a problem. Initially, the position of the
dollar as a reserve currency and the confidence generated by the military
strength of the US made it a safe haven for wealthholders across the global.
Dollar-denominated assets attracted the world's capital and not just financed
the US current account deficit but also fuelled a stock market boom. Subsequently,
countries that had accumulated large foreign reserves either because of
they were successful exporters or because their imports had been curtailed
by deflation, invested these reserves in dollar assets, especially US
Treasury bonds, and helped finance the external deficit. The dollar remained
strong despite the current account deficit.
The difficulty is that underlying such confidence of public and private
investors is the view that the trade and current account deficits in the
US would somehow take care of themselves, without damaging US growth substantially.
Unfortunately, while growth has been better in the US than in the euro
area and Japan, the deficit has not disappeared but ballooned. In the
circumstance, the only way of curtailing the US trade deficit seems to
be to curtail growth - either by depressing consumer spending or by slashing
the fiscal deficit or both. President Bush and his team were unwilling
to concede on either count prior to his re-election. And the evidence
seems to be that he is not going to immediately wipe clean the glory his
victory has brought by declaring war on US buoyancy.
Bush is not the only one who is unwilling to spoil the party. Alan Greenspan,
who nears the finish of what appeared to be an unending tenure, has warned
that the US current account deficit is unsustainable. But he too has not
shown any keenness to raise interest rates to scorch consumption and investment
spending. What is more, countries which have gained from the US predicament
in the form of large exports to the US market - such as China - are also
not in favour of a US slowdown.
The US has sought to use the last of these by virtually declaring that
its own deficit is not its, but the world's, problem. Countries like China
with a large trade surplus with the US must revalue their currencies upwards
to redress that trade imbalance by exporting less to and importing more
from the US. Other countries, such as those in Europe need to reflate
their economies so as to expand markets for the US. And, finally, all
countries must open doors to their markets by reducing tariffs, so that
the US can ship in more of its commodities. All this, in the US government
view, would help reduce its current account deficit and stabilise the
dollar, without affecting US and, therefore, global growth.
None of these countries are willing to toe that line. China, under pressure
to permit an appreciation of the yuan, has come out quite strongly. In
an interview with the Financial Times, Li Ruogu, the deputy governor of
the People's Bank of China, warned the US not to blame other countries
for its economic difficulties. "China's custom is that we never blame
others for our own problem," he reportedly said. "For the past
26 years, we never put pressure or problems on to the world. The US has
the reverse attitude, whenever they have a problem, they blame others."
At the recent G20 meeting, finance ministers and central bank governors
called for a global effort to reduce trade imbalances, and in particular,
the US current account deficit. The rhetoric seemed to be that everybody
should share the costs of that adjustment. John Snow, the US treasury
secretary, chipped in by promising to work towards halving the US budget
deficit and increasing US national saving. But no concrete measures were
on offer.
In sum, there is a degree of global paralysis on the issue of the US deficit
and its impact on global growth. This implies that the only way in which
the external deficit may stop rising and possibly decline is through a
downward adjustment of the dollar, which renders imports into the US expensive
and cheapens US exports.
However, an adjustment of the dollar has been underway not so much because
of any automatic responsiveness to US trade trends, but because of a growing
fear among wealth holders that excess exposure to dollar denominated assets
threatens erosion of the value of that wealth. The gradual adjustment
of private portfolios explains the dollar's decline in the past. More
recently, however, pressure from the dollar has come from a different,
and more powerful, source: the growing unwillingness of central banks
to hold a disproportionate quantity of dollar reserves and risk substantial
losses.
Russian central bank officials have recently declared that they are likely
to adjust the structure of its reserves, estimated at around $105 billion,
by substantially reducing the share of the dollar. Even a small country
like Indonesia with just $35 billion dollars of reserves has threatened
to cut its dollar holding. But the real threat comes from China with $515
billion in its chest and Japan, which together account for the bulk of
Asia $2.3 billion of reserves. A recent statement by a Chinese academic,
which was quickly retracted, that the rate of increase of China's holdings
of US bonds had fallen and the total was now around $180 billion, was
enough to trigger a slump in the dollar in jittery markets.
If this trend for policy makers in the US and elsewhere to wait-and-watch
and for wealthholders and central banks to turn cautious on the dollar
persists, the downward slide of the currency is likely to accelerate.
Unfortunately, this would help no one. The appreciation of the euro and
the yen would affect their exports. The slowing of growth in the US that
an enforced cutback in government and private spending and inflation induced
by a falling dollar would result in, would hurt most exporters, including
those from China. And a possible meltdown in US markets is bound to wipe
out a huge quantity of paper wealth that sustains even the current level
of business confidence. Above all, the fragility in financial markets
that the process generates can trigger a liquidity crunch that would spell
deflation.
The fundamental problem is that countries desperate to accelerate or protect
the growth of their own markets and exports, are unwilling to come together
to deal with what is not just a US problem. And their failure to do so
hurts not just the US but the world economy as a whole.
These contradictions in the current global conjuncture reflect the peculiar
nature of US leadership. That leadership is no more attributable to the
relative strength of the US economy, but rather is explained by the military
might of the US and its self-assumed role of global policeman. However,
despite the lack of US economic supremacy, there is a bias to bilateralism
in the global system. The US remains an important market for most countries,
especially the successful exporters like China in goods and India in services.
The US has also been the most favoured destination for financial investment
for private wealthholders and governments.
If countries want this cosy but undeclared relationship with the US to
continue they are bound to be asked to pay a price for the militarism
that makes the US a buoyant economy, a sponge for global exports and a
safe haven for investment. If they are unwilling, they must seek out strategies
that break this undeclared bias to bilateralism that is reminiscent of
colonial times. That would spell an end to US supremacy and the emergence
of a truly multipolar world. However, the transition is not guaranteed.
The costs are likely to be substantial and the outcomes are uncertain.
But perhaps the dollar conundrum signals that there are no mutually acceptable
choices left.